Page 234 - Annual Report 2019-20
P. 234
notes forming part of the consolidated financial statements Notes forming part of the consolidated financial statements 233
( in crores)
JpY impact (F) Credit risk management
For the For the Credit risk refers to risk that a counterparty will default on its contractual obligations resulting in financial loss to the Group.
year ended year ended Credit risk arises primarily from financial assets such as trade receivables, investment in mutual funds, derivative financial PIDILITE ANNUAL REPORT 2019-20
31 March 31 March instruments, other balances with banks, loans and other receivables
st
st
2020 2019 The Group has adopted a policy of only dealing with counterparties that have sufficiently high credit rating. The Group’s
Impact on profit or loss for the year (refer note c) (0.01) (0.01) exposure and credit ratings of its counterparties are continuously monitored and the aggregate value of transactions is
reasonably spread amongst the counterparties.
(a) This is mainly attributable to the exposure of outstanding uSD receivables and payables at the end of the reporting Credit risk arising from investment in mutual funds, derivative financial instruments and other balances with banks is limited
period. and there is no collateral held against these because the counterparties are banks and recognised financial institutions with
high credit ratings assigned by the international credit rating agencies.
(b) This is mainly attributable to the exposure of outstanding EuR receivables and payables at the end of the reporting
period. (G) Liquidity risk management
(c) This is mainly attributable to the exposure of outstanding JPy payables at the end of the reporting period. Liquidity risk is the risk that the Group will encounter difficulty in raising funds to meet commitments associated with
financial instruments that are settled by delivering cash or another financial asset. Liquidity risk may result from an inability
In management’s opinion, the sensitivity analysis is unrepresentative of the inherent foreign exchange risk because the to sell a financial asset quickly at close to its fair value.
exposure at the end of the reporting period does not reflect the exposure during the year. The Group has an established liquidity risk management framework for managing its short term, medium term and long term
(ii) Foreign exchange forward contracts funding and liquidity management requirements. The Group’s exposure to liquidity risk arises primarily from mismatches of
the maturities of financial assets and liabilities. The Group manages the liquidity risk by maintaining adequate funds in cash
It is the policy of the Group to enter into foreign exchange forward contracts to cover foreign currency payments (net and cash equivalents. The Group also has adequate credit facilities agreed with banks to ensure that there is sufficient cash
of receipts) in uSD, EuR, GBP and AuD. The Group enters in to contracts with terms upto 90 days. to meet all its normal operating commitments in a timely and cost-effective manner.
The Group’s philosophy does not permit any speculative calls on the currency. It is driven by conservatism which guides (i) Liquidity risk tables
that we follow conventional wisdom by use of Forward contracts in respect of Trade transactions.
Regulatory Requirements: The Group will alter its hedge strategy in relation to the prevailing regulatory framework and The following tables detail the Group's remaining contractual maturity for its derivative and non-derivative financial liabilities
guidelines that may be issued by RBI, FEDAI or ISDA or other regulatory bodies from time to time. with agreed repayment periods. The tables have been drawn up based on the undiscounted cash flows of financial liabilities
based on the earliest date on which the Group can be required to pay. The tables include both interest and principal cash
Mode of taking Cover: Based on the outstanding details of import payable and exports receivable (in weekly baskets) flows. To the extent that interest flows are floating rate, the undiscounted amount is derived from interest rate curves at the
the net trade import exposure is arrived at (i.e. Imports – Exports = net trade exposures). end of the reporting period.
The net trade import exposure arrived at is netted off with the outstanding forward cover as on date and with the ( in crores)
surplus foreign currency balance available in EEFC A/Cs.
Less than 1 1-5 years More than 5 Total Carrying Amount
Forward cover is obtained from bank for each of the aggregated exposures and the Trade deal is booked. The forward year years
cover deals are all backed by actual trade underlines and settlement of these contracts on maturity are by actual As at 31 March 2020
st
delivery of the hedged currency for settling the underline hedged trade transaction.
Non-interest bearing
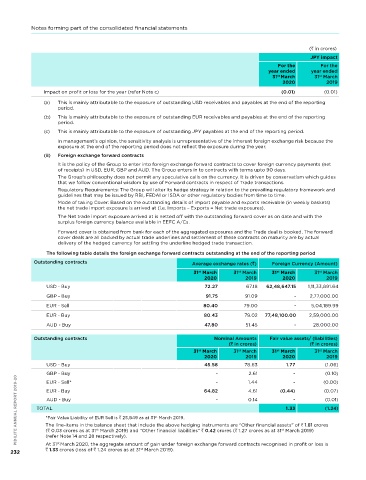
The following table details the foreign exchange forward contracts outstanding at the end of the reporting period - Trade Payables 621.01 - - 621.01 621.01
Outstanding contracts Average exchange rates ( ) Foreign Currency (Amount) - Other Financial Liabilities 456.06 7.26 - 463.32 463.32
st
st
st
st
31 March 31 March 31 March 31 March 1,077.07 7.26 - 1,084.33 1,084.33
2020 2019 2020 2019 - Lease Liabilities (undiscounted) 35.13 66.89 48.93 150.95 111.47
uSD - Buy 72.27 67.18 62,48,647.15 1,11,33,891.64 Fixed interest rate instruments
GBP - Buy 91.75 91.09 - 2,77,000.00 - Trade/ Security Deposit received 123.93 - - 123.93 123.93
EuR - Sell 80.40 79.00 - 5,04,189.99 Variable interest rate instruments
- Borrowings 143.99 25.13 - 169.12 169.12
EuR - Buy 80.43 79.02 77,48,100.00 2,59,000.00
- Current Maturity of Term Loan 7.10 - - 7.10 7.10
AuD - Buy 47.80 51.45 - 28,000.00
Derivative liabilities towards foreign 0.42 - - 0.42 0.42
exchange forward contracts
Outstanding contracts Nominal Amounts Fair value assets/ (liabilities)
( in crores) ( in crores) Gross obligation towards acquisition - 81.23 - 81.23 81.23
st
31 March 31 March 31 March 31 March As at 31 March 2019
st
st
st
st
2020 2019 2020 2019 Non-interest bearing
uSD - Buy 45.58 78.63 1.77 (1.06) - Trade Payables 580.64 - - 580.64 580.64
-
-
GBP - Buy 64.82 1.44 (0.44) (0.00) - Fixed interest rate instruments 384.30 9.81 - 974.75 974.75
(0.10)
2.61
Other Financial Liabilities
394.11
394.11
PIDILITE ANNUAL REPORT 2019-20 TOTAL st st - 0.14 st 1.33 (1.24) - Variable interest rate instruments 109.96 8.51 - 109.96 109.96
EuR - Sell*
-
-
-
9.81
964.94
(0.07)
4.61
EuR - Buy
-
Trade/ Security Deposit received
AuD - Buy
(0.01)
-
102.54
111.05
-
-
111.05
Borrowings
*Fair Value Liability of EuR Sell is 25,849 as at 31 March 2019.
-
-
1.69
-
Current Maturity of Term Loan
1.69
1.69
The line-items in the balance sheet that include the above hedging instruments are “Other financial assets” of 1.81 crores
( 0.03 crores as at 31 March 2019) and “Other financial liabilities” 0.42 crores ( 1.27 crores as at 31 March 2019)
1.27
1.27
1.27
Derivative liabilities towards foreign
-
At 31 March 2020, the aggregate amount of gain under foreign exchange forward contracts recognised in profit or loss is
st
Gross obligation towards acquisition
1.33 crores (loss of 1.24 crores as at 31 March 2019).
232 (refer note 14 and 28 respectively). st exchange forward contracts - 76.17 - 76.17 76.17